
Machining
The following page of notes will cover:
- Vertical milling
- Horizontal milling
- Routing
- Drilling
- Turning
- Stamping
- Pressing
Vertical milling:
How it works:
- Material is clamped into place
- Cutter is selected and RPM is chosen
- The material always remains stationary while the machines cutting tool rotates
- As the cutting moves, it presses against the workpiece and shapes the material
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Uses: Cutting gears, produce slots, drilling
Horizontal milling:
How it works:
- Material is clamped into place
- Cutter is selected and RPM is chosen
- The material always remains stationary while the machines cutting tool rotates
- As the cutting moves, it presses against the workpiece and shapes the material
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Uses: Cuttings gears, produce slots, drilling
Routing:
How it works:
- Material is clamped into place
- Cutter is selected and RPM is chosen
- The material always remains stationary while the machines cutting tool rotates
- As the cutting moves, it presses against the workpiece and shapes the material
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Uses: Cabinets, doors
Drilling:
How it works:
- Drill bit is selected and holes are marked up
- Drill bit is fixed in the chuck and tightened using a chuck key
- The table is set at a certain height and the RPM of the drill is chosen
- The hand wheel is lowered to drill the hole
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Uses: Drilling holes for products, seperating pop rivets
Turning:
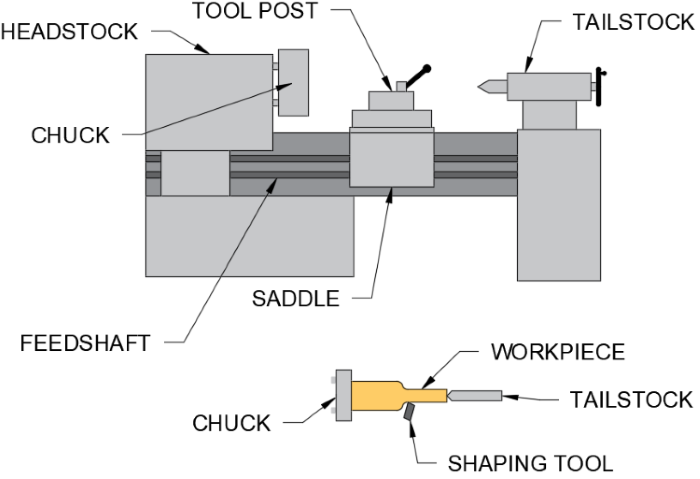
How it works:
- Begin by placing a circular, square or rectangular shaped peice of metal/wood into the lathes drive area
- The metal/wood piece is typically secured using a pressure pad
- Once in place, the lathe is activated to rotate and press the mould against the metal/wood piece
- The rotational force of the lathe then deforms the metal/wood piece to achieve the same shape as the mould
- When metal/wood spinning is performed by hand, a worker manually presses the mould against metal/wood piece
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Uses: Table legs, table lamp, engine parts, handles
Note: Turning machines are different depending on the material being used.
Stamping:
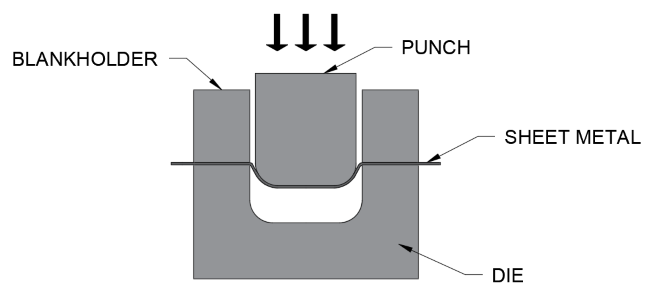
How it works:
- Process is usually done via a CNC
- The CNC program moves the platen carrying the sheet metal
- Once the sheet metal is under the stamp the die is punched against the sheet metal
- The waste material is then recycled and the stamped metal is collected
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Uses: Shape sheet metal into shapes with holes, washers, cogs, tin can pull tabs
Pressing:
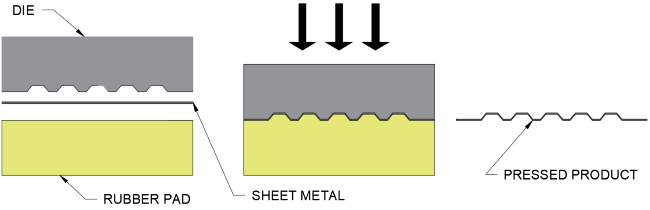
How it works:
- Metal is rolled out and straightened
- Metal is cut to required blank size
- The blank metal is clamped over the die and held in the correct position using the back gauge
- A hydraulically operated punch is then pushed into the sheet metal
- Once the desired shape is formed the punch is retracted and the sheet component is ejected
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|